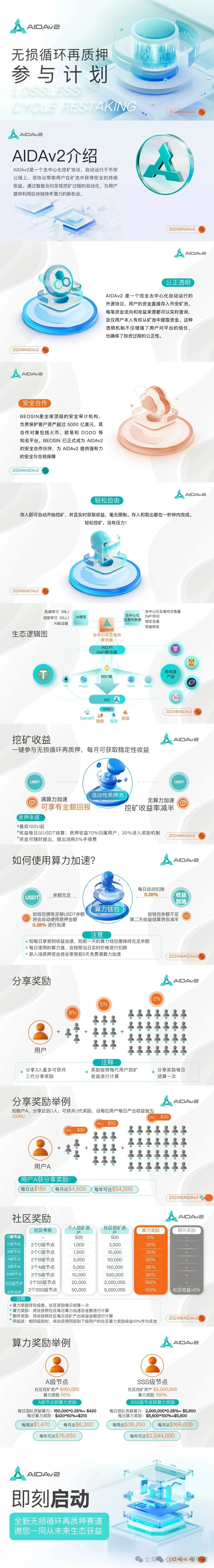
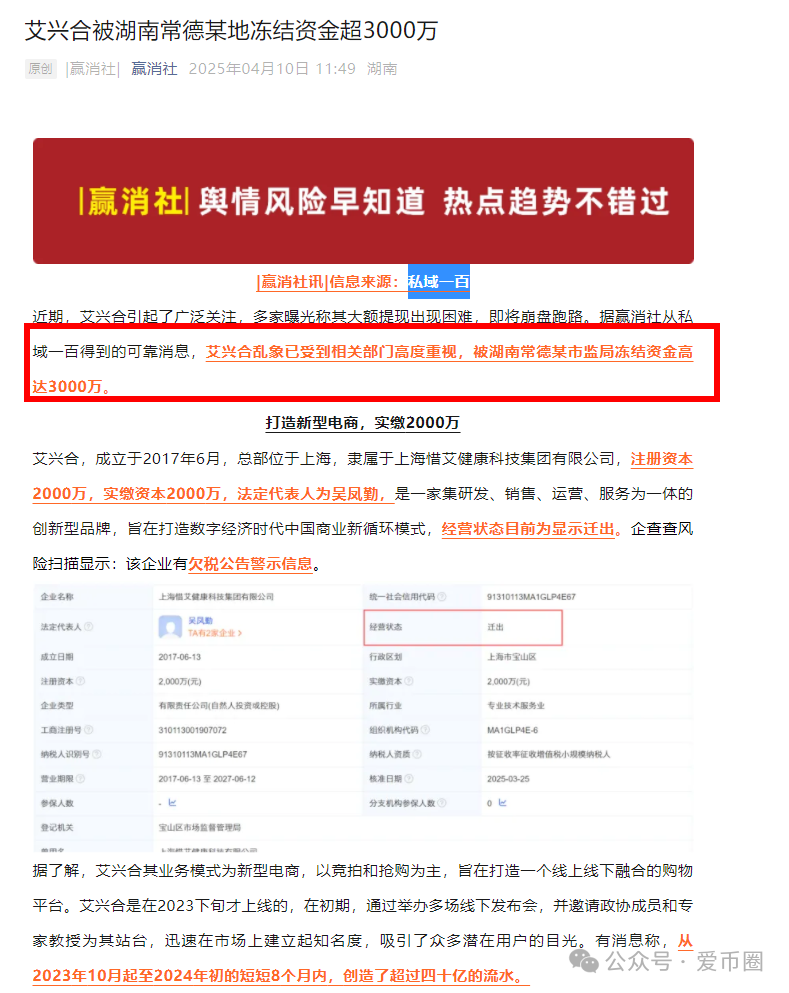
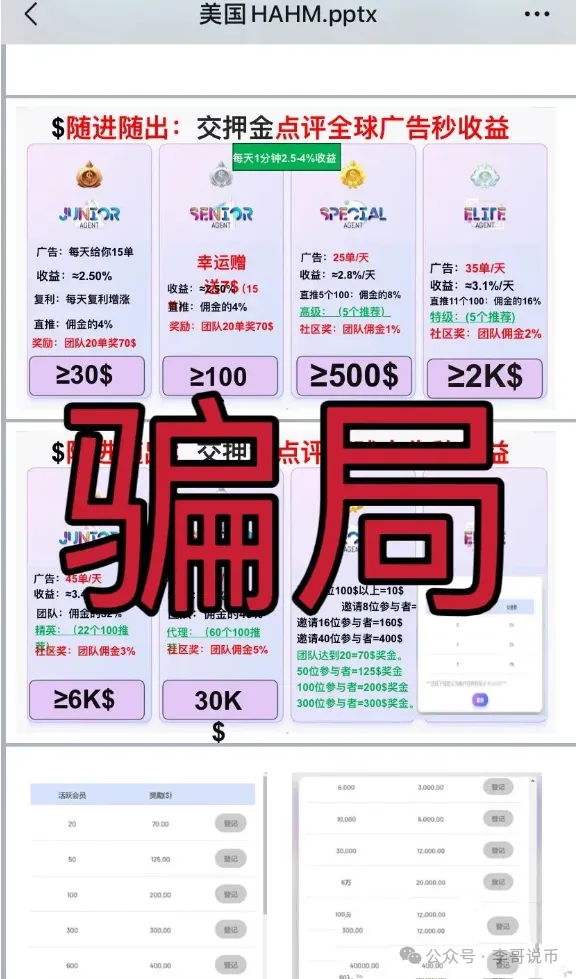
WTF is Ethereum?
The ultimate guide to understand why Ethereum is not just another cryptocurrency.
了解为什么以太坊不只是另一种加密货币的终极指南
Although ‘Bitcoin’ and ‘Ethereum’ are terms that are often paired together, the reality is that they are vastly different. The only thing Ethereum shares with Bitcoin is that it’s a cryptoasset running on top of blockchain.
Instead of being just a cryptocurrency, like Bitcoin, Ethereum also has features which effectively makes it a huge decentralized computer.
虽然’比特币’和’以太坊’是经常被搭配在一起的术语,但现实是它们有很大的不同。以太坊与比特币的唯一共同点是,它是一种运行在区块链之上的加密资产。
与比特币一样,以太坊不仅仅是一种加密货币,它还具有一些功能,这些功能实际上使它成为一个巨大的去中心化的计算机。
要了解以太坊,必须了解区块链的工作原理。如果你已经了解了,或者已经读过我的了解区块链的终极指南,请放心直接进入下一节。
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain, simply put, is a database. It’s an ever growing database of certain kind of data and has quite remarkable properties:
1.Once data is stored in the database, it can never be modified or deleted. Every record on a blockchain is permanent for eternity.
2.No single individual or organization maintains the database; several thousand individuals do, and everyone has a copy of the database with themselves.
什么是区块链?
区块链,简单地说,就是一个数据库。它是一个不断增长的某种数据的数据库,具有相当显著的特性。
1. 一旦数据被存储在数据库中,它就永远不能被修改或删除。区块链上的每条记录都是永久的,是永恒的。
2.没有一个人或组织维护数据库;几千个人在维护,每个人都有一份数据库的副本。
To understand how several people are able to keep their copies of the database in sync with everyone else, imagine there are ten individuals in a network. Everyone is sitting with an empty file folder and an empty page in front of them. Whenever anyone does something important in the network, like transferring money, they announce it to everyone in the network.
为了理解几个人如何能够使他们的数据库副本与其他人保持同步,想象一下在一个网络中有十个人。每个人面前都坐着一个空文件夹和一个空页面。每当有人在网络中做一些重要的事情,比如转账,他们就会向网络中的每个人宣布。
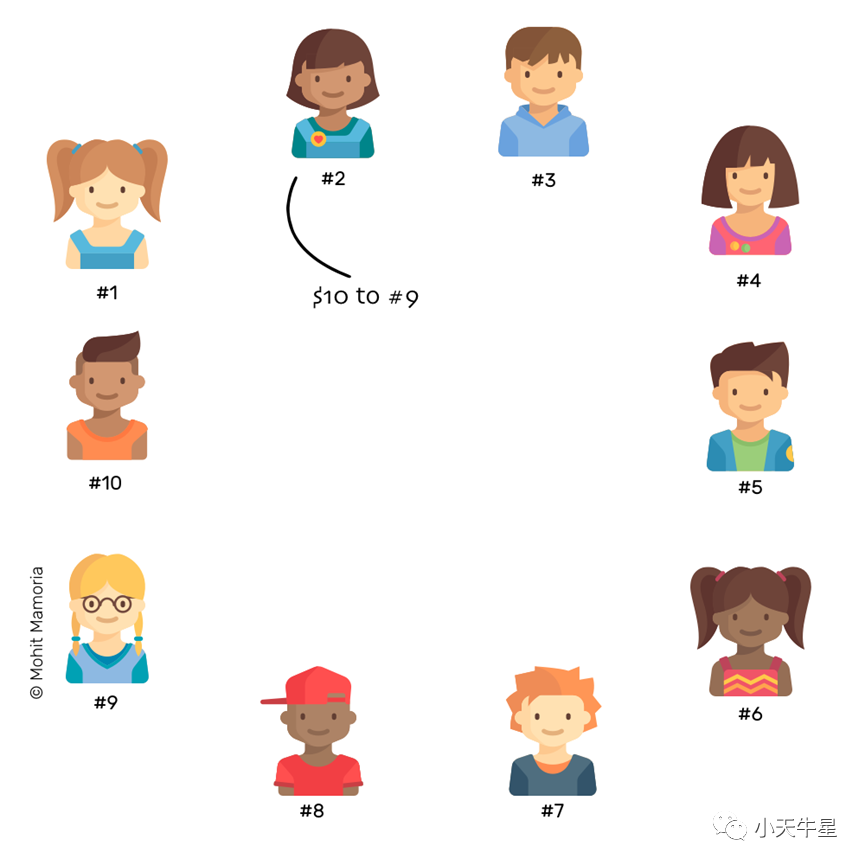
Everyone makes a note of the announcement on their pages until the page is filled. When it does, everyone has to seal the contents of the page by solving a mathematical puzzle. Solving the mathematical puzzle ensures that everyone’s page had same contents and that they can never be modified. Whoever does it first, gets rewarded with some amount of cryptocurrency.
每个人都在自己的页面上记下公告的内容,直到页面被填满。当它被填满时,每个人都必须通过解决一个数学谜题来密封页面的内容。解决这个数学谜题可以确保每个人的页面都有相同的内容,并且永远不会被修改。谁先做到这一点,谁就能得到一定数量的加密货币的奖励。
Once the page is sealed, the page is added to the file folder, a new page is brought out and the process continues forever.
一旦这一页被封存,这一页就会被添加到文件夹中,新的一页就会被拿出来,这个过程会永远继续下去。
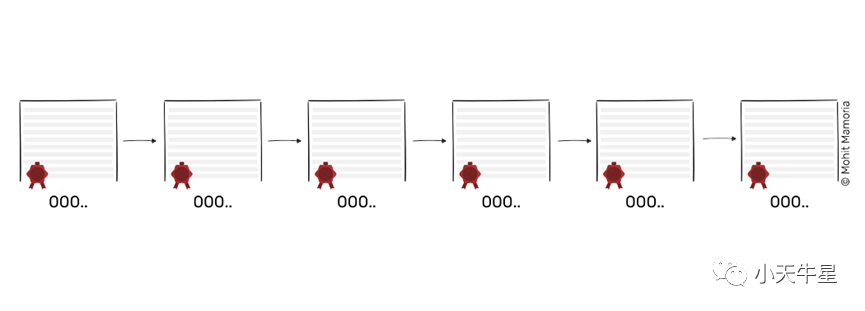
Blockchain
As time passes, these pages (blocks) that contain important records (transactions) are added to the folder (chain), thus forming the database (blockchain).
随着时间的推移,这些包含重要记录(交易)的页面(区块)被添加到文件夹(链)中,从而形成数据库(区块链)。
What does a blockchain store?
A blockchain can be used to store any kind of data, and the kind of data a blockchain stores, gives it its value. Bitcoin’s blockchain stores the records of financial transactions, therefore, making it analogous to a currency like dollars or pounds. Bitcoins serve no additional purpose than what dollars serve. Ethereum is different.
Ethereum is not merely a currency like dollars, pounds or bitcoin. Ethereum has a purpose higher than just being a currency. Ethereum is this:
区块链存储什么?
区块链可以用来存储任何种类的数据,而区块链所存储的数据种类,使其具有价值。比特币的区块链存储的是金融交易的记录,因此,使其类似于美元或英镑这样的货币。比特币没有比美元更多的用途。以太坊则不同。
以太坊不仅仅是一种像美元、英镑或比特币一样的货币。以太坊有一个比仅仅作为货币更高的目的。以太坊就是这样。

Ethereum is basically a huge computer! However it’s an extremely slow one — about five to 100 times slower than regular computers today — and very expensive. The ‘Ethereum computer’ has about the same power as one of the rare90’s smartphones; so it can’t really do much more than some very trivial things.
以太坊基本上是一个巨大的计算机!但它是一个非常慢的计算机–比今天的普通计算机慢5-100倍,而且非常昂贵。以太坊电脑 “的功率与90年代罕见的智能手机之一差不多;因此,除了一些非常琐碎的事情,它真的不能做得更多。
That doesn’t really sound so impressive, so why is there so much hype around Ethereum? Well, that’s a really good question. Ethereum is taking the world by storm because it’s a completely decentralized computer that is distributed across the globe. Understanding how Ethereum’s blockchain works will reveal how it acts like a world computer.
这听起来并不那么令人印象深刻,那么为什么以太坊周围有这么多的炒作呢?嗯,这真是个好问题。以太坊正在风靡世界,因为它是一个完全去中心化的计算机,分布在全球各地。了解以太坊的区块链是如何工作的,将揭示它是如何像世界计算机一样行事的。
How does Ethereum work?
Like any other blockchain, Ethereum needs several thousand people running a software on their computers to power the network. Every node (computer) in the network runs something called Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Think of EVM as a operating system that understands and executes the software written in Ethereum specific programming language. The software/apps executed by Ethereum Virtual Machine are called ‘smart contracts.’
以太坊是如何工作的?
像其他区块链一样,以太坊需要几千人在他们的电脑上运行一个软件来驱动网络。网络中的每个节点(计算机)都运行着一种叫做以太坊虚拟机(EVM)的东西。把EVM想象成一个操作系统,理解并执行以太坊特定编程语言编写的软件。由以太坊虚拟机执行的软件/应用程序被称为 “智能合约”。
To get anything done on this world computer, you need to pay a price. However, you don’t pay it in regular currency like dollars or pounds. Instead, everything has to be paid with a cryptocurrency native to the network, called ether. Ether is exactly like bitcoin except that it can also be used to pay for executing smart contracts on Ethereum.
要在这个世界的电脑上完成任何事情,你需要付出代价。然而,你不是用美元或英镑等常规货币支付。相反,一切都必须用网络中原生的加密货币支付,称为以太币。以太币与比特币完全一样,只是它也可以用来支付执行以太坊的智能合约。
A human being and a smart contract are both seen as users on Ethereum. Whatever a human user can do, a smart contract can do too, and then some.
人类和智能合约都被视为以太坊的用户。人类用户能做的事,智能合约也能做,甚至更多。
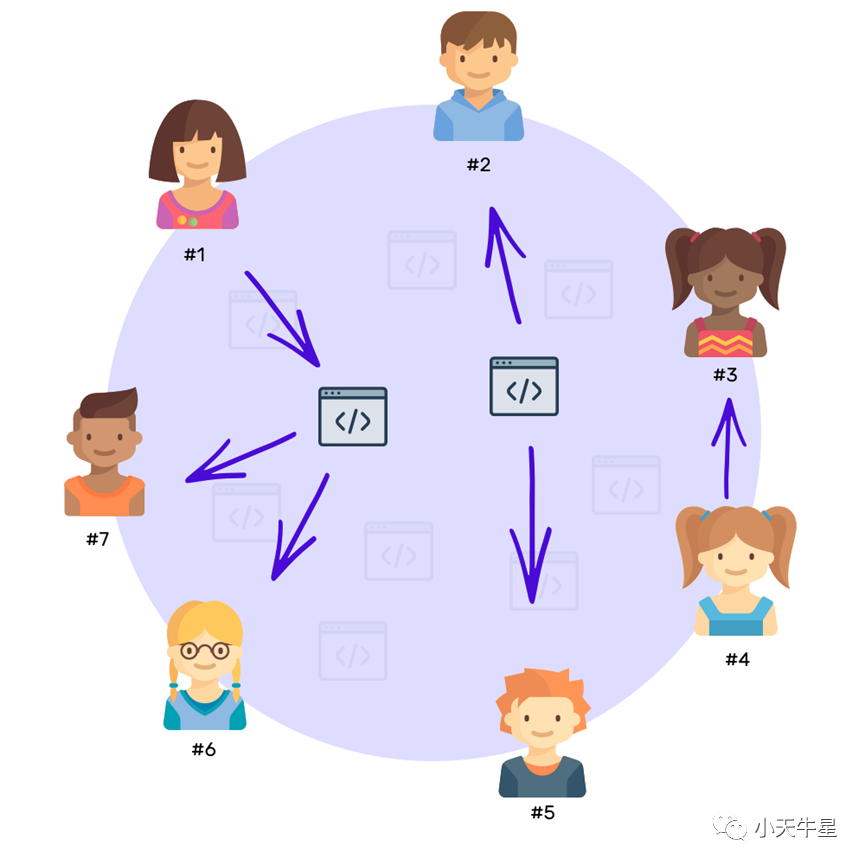
Smart contracts act exactly like any other human user in the network. Both of them can send and receive ether just like any other currency.
智能合约的行为与网络中的其他人类用户完全一样。他们都可以像其他货币一样发送和接收以太币。
But unlike human users, smart contracts can also execute a predefined computer program to perform various actions when triggered. To understand the power of a smart contract, let’s consider an example.
但与人类用户不同的是,智能合约也可以执行预定义的计算机程序,在被触发时执行各种行动。为了理解智能合约的力量,让我们考虑一个例子。
Power of smart contracts
Imagine you and I place a bet about tomorrow’s weather. I bet that it’ll be sunny tomorrow while you bet it’ll be rainy. We agree that the loser has to give the winner $100. How can we do this and ensure that the loser will keep his promise? I can think of three distinct ways:
智能合约的力量
想象一下,你和我就明天的天气打了个赌。我打赌明天会是晴天,而你打赌会是雨天。我们约定,输家必须给赢家100美元。我们怎样才能做到这一点,并确保输家会遵守承诺呢?我可以想到三种不同的方法。
1. Trust each other
The simplest way to do this would be to trust each other. If we’ve been friends for a long time now, trusting each other is pretty easy. I know where you live and you know all kinds of embarrassing stuff about me. But things get more difficult if we’re complete strangers. You have no reason to trust me and I have no reason to trust you.
1. 互相信任
最简单的方法是相互信任。如果我们现在已经做了很长时间的朋友,信任对方是很容易的。我知道你住在哪里,你也知道关于我的各种令人尴尬的事情。但如果我们是完全陌生的人,事情就会变得更加困难。你没有理由相信我,我也没有理由相信你。
2. Sign a legal agreement
Another plausible way is to formulate our bet as a legal agreement. We’ll both sign an agreement that defines all the terms of our bet in detail — including what happens if the loser violates the agreement.
The agreement would makes us legally obligated to pay the winner, but it wouldn’t serve any practical purpose because forcing the agreement through the legal route would be more expensive than what the bet was worth.
2. 签署一份法律协议
另一个合理的方法是将我们的赌注拟定为一份法律协议。我们双方将签署一份协议,详细定义我们赌注的所有条款–包括如果输家违反协议会发生什么。
该协议将使我们在法律上有义务支付赢家,但它不会起到任何实际作用,因为通过法律途径强制执行该协议的费用会比赌注的价值更高。
3. Get help from a mutual friend
We could find a mutual friend who we both trust and we’d both give him/her $100 each for safekeeping. The nextday, he/she would check the weather and give the total $200 to whoever won the bet. Simple and easy, except that it isn’t: What if the trusted friend runs away with $200?
Now we have three different ways of doing the bet but each option has its shortcomings. Because we are strangers, we cannot trust each other. Forcing a legal agreement will be so expensive that it wouldn’t be practically feasible. Getting help from a mutual friend brings up the question of trust again.
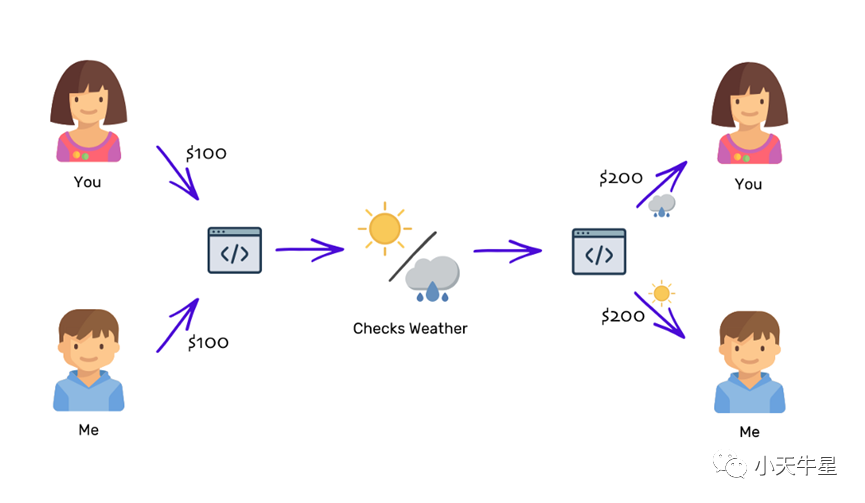
Ethereum’s smart contract can save the day in such a situation. A smart contract is like the trusted mutual friend but written in code. Ethereum allows us to write a software that accepts ether worth $100 from both of us, and then the next day, uses the open weather API to check the weather and transfer the total ether worth of $200 to the winner.
3. 从一个共同的朋友那里获得帮助
我们可以找到一个共同的朋友,我们都信任他/她,然后我们都给他/她每人100美元作为保管费。第二天,他/她会检查天气,并将总额200美元交给赢得赌局的人。简单而容易,除了它不是。如果那个值得信赖的朋友拿着200美元跑了怎么办?
现在我们有三种不同的打赌方式,但每个选项都有其缺点。因为我们是陌生人,我们不能信任对方。强行签订法律协议的费用会很高,实际上是不可行的。从共同的朋友那里获得帮助又带来了信任的问题。
在这种情况下,以太坊的智能合约可以拯救世界。智能合约就像受信任的共同朋友,但用代码编写。以太坊允许我们写一个软件,接受我们两个人的价值100美元的以太坊,然后在第二天,使用开放的天气API检查天气,并将总价值200美元的以太坊转移给赢家。
Once a smart contract has been written it cannot be edited or altered in any way. Therefore, you can be sure that whatever the contract dictates, it will be executed no matter what.
But how is a smart contract executed? And how does it relate to blockchain?
一旦智能合约被写入,它就不能以任何方式被编辑或改变。因此,你可以确信,无论合同规定什么,它都会被执行。
但智能合约是如何执行的?它与区块链又有什么关系?
How does smart contract relate to blockchain?
Whenever a smart contract is executed, it records the information about the execution on a block as a transaction. On a very high level, a transaction on Ethereum blockchain looks like this:
智能合约与区块链的关系如何?
每当智能合约被执行时,它就会把执行的信息记录在一个区块上,作为一个交易。在一个非常高的水平上,以太坊区块链上的交易看起来像这样。
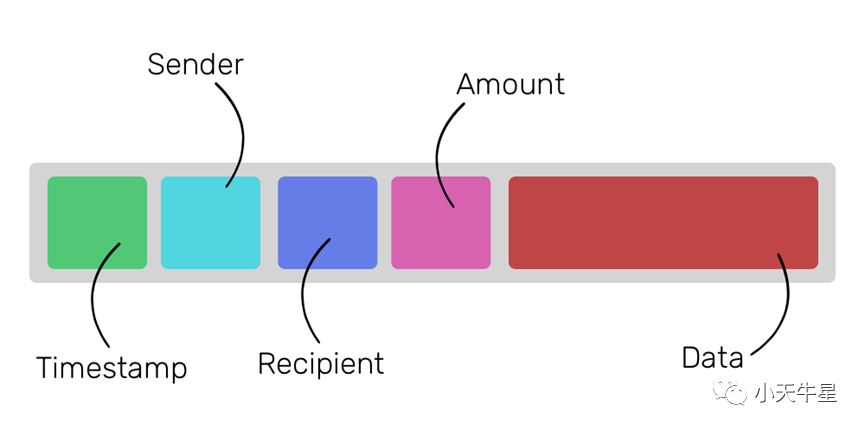
The fields are self explanatory except the last one. The ‘data’ field is what gives Ethereum its unique power. The ‘data’ field is used to record creation and execution of smart contracts as a transaction. Any given block on the Ethereum blockchain can contain three kind of transactions:
除了最后一个字段,其他字段都是不言自明的。数据 “字段是赋予Ethereum独特力量的原因。数据 “字段被用来记录智能合约的创建和执行,作为一项交易。以太坊区块链上的任何特定区块可以包含三种交易。
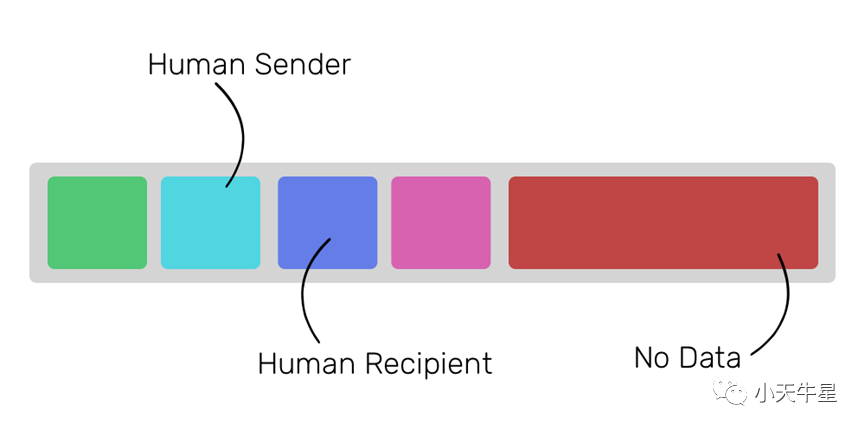
1. Regular transfers of ether from one user to a human user
These are the regular bitcoin-like transactions in the network. If you send ether directly to your friend the data field will be left empty.
1. 一个用户向一个人类用户定期转移以太币
这些是网络中类似比特币的常规交易。如果你直接向你的朋友发送以太币,数据字段将被留空。
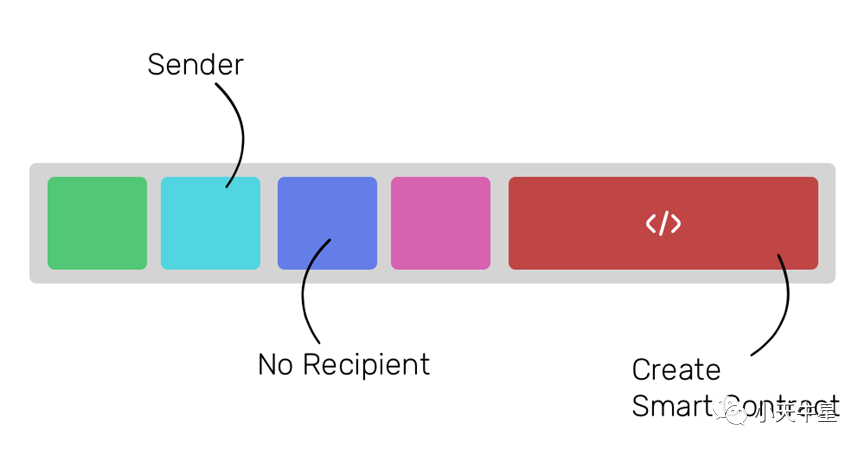
2. Transfers of ether from one user to no one
When a transaction without a recipient is made, it means that the purpose of the transaction is to create a smart contract in the network using the contents present in the ‘data’ field. The ‘data’ field contains the software code that will be made to act like any other user in the network.
2. 从一个用户转移到没有人的地方的以太币
当一个没有收件人的交易发生时,这意味着该交易的目的是在网络中使用’数据’字段中存在的内容创建一个智能合约。数据 “字段包含的软件代码将被制成与网络中任何其他用户一样的行为。
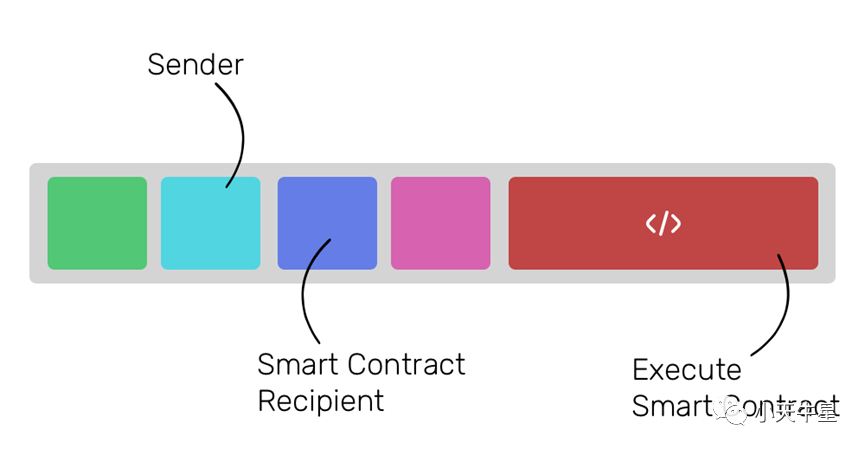
3. Transfers of ether from a user to a smart contract
Whenever a user (or a smart contract) wants to execute a smart contract, he/she/it is required to make a transaction to the smart contract and put the instructions for the execution in the ‘data’ field.
3. 从一个用户到一个智能合约的以太币转移
每当一个用户(或一个智能合约)想要执行一个智能合约,他/她/它需要向智能合约进行交易,并将执行指令放在 “数据 “字段中。
Just like in any other blockchain, whenever any of the three events mentioned above happen, it’s announced to the whole network and everyone makes a note of it. In addition to making note of it, each node also executes the instructed smart contract to bring the state of their EVM in sync with the rest of the network.
Each node executes a piece of software, thus, making the whole network act as a giant (but slow) distributed computer. Every tiny execution is then stored on the blockchain to make it permanent.
就像其他区块链一样,每当上述三个事件中的任何一个发生,都会向整个网络宣布,每个人都会记下它。除了记下它之外,每个节点还执行指示的智能合约,使其EVM的状态与网络的其他部分同步。
每个节点执行一个软件,因此,使整个网络作为一个巨大的(但缓慢的)分布式计算机。然后,每一个微小的执行都被储存在区块链上,使其成为永久性的。
Wait, I’ve heard about something called Gas — what’s that?
I told you that the user using a smart contract must pay a certain price to execute it. This price is paid to the node that actually spends memory, storage, computation and electricity to execute the smart contract.
等等,我听说过一个叫Gas的东西–那是什么?
我告诉你,使用智能合约的用户必须支付一定的价格来执行它。这个价格是支付给实际花费内存、存储、计算和电力来执行智能合约的节点的。
To calculate the prices of smart contracts, every statement has an assigned cost to it. For example, if you execute a statement that uses the node’s memory, those type of statements have a specific cost. If you execute a statement that uses the node’s disk storage, those kind of statements have a specific cost attached to them. The unit in which the cost is defined is called Gas. Eventually, Gas is converted to ether using an exchange rate.
为了计算智能合约的价格,每个语句都有一个分配的成本。例如,如果你执行一个使用节点内存的语句,那些类型的语句有一个特定的成本。如果你执行一个使用节点的磁盘存储的语句,那些类型的语句有一个特定的成本附加在它们身上。定义成本的单位被称为Gas。最终,Gas通过一个汇率被转换为以太币。
Whenever you execute a smart contract, you have to define the maximum Gas to be consumed. The execution will stop either when the execution is completed or when the Gas Limit is reached. This is done to avoid infinite loops in smart contracts, preventing the program getting stuck executing a set of statements repeatedly without proceeding further.
每当你执行一个智能合约时,你必须定义所要消耗的最大气体。当执行完成或达到Gas Limit时,执行将停止。这样做是为了避免智能合约中的无限循环,防止程序被卡住重复执行一组语句而无法继续下去。
Such situations occur because of programmer’s carelessness. With every repetition, some of the assigned Gas will be used, thus making any infinite loop a finite one. It doesn’t make any sense for a node to be stuck in execution because of a programmer’s mistake. The concept of Gas solves this problem.
这种情况的发生是因为程序员的粗心。随着每一次重复,一些分配的Gas将被使用,从而使任何无限循环成为有限循环。一个节点因为程序员的错误而被卡在执行中是没有任何意义的。气体的概念解决了这个问题。
And that, ladies and gentleman, is Ethereum
Ethereum isn’t just a cryptocurrency to be traded; its real value lies in its purpose. Ethereum’s purpose is to allow the owner to use the distributed world computer that several thousand nodes are powering.
Of course, because every tiny statement has to be executed by every node in the network, the decentralized, distributed computer becomes slow and expensive. But slow compared to what? The faster but centrally controlled servers.
To enjoy the lower costs of using a centralized computer, we give them the power to control us. If the central computer (server) goes down or gets hacked, it takes down with it all the clients attached to it. A decentralized computer will only go down if every single node goes down, making it a computer that will always be available. Wherever there’s internet, there’s Ethereum.
而这,女士们,先生们,就是以太坊
以太坊不仅仅是一种可以交易的加密货币;它的真正价值在于其目的。以太坊的目的是允许所有者使用几千个节点所提供的分布式世界计算机。
当然,由于每一个微小的语句都必须由网络中的每一个节点来执行,去中心化的分布式计算机变得缓慢而昂贵。但是,与什么相比慢呢?更快但集中控制的服务器。
为了享受使用集中式计算机的低成本,我们给了他们控制我们的权力。如果中央计算机(服务器)瘫痪或被黑客攻击,它就会连带着所有连接在它上面的客户端一起瘫痪。一个分散的计算机只有在每个节点都瘫痪的情况下才会瘫痪,这使得它成为一个永远可用的计算机。只要有互联网的地方,就有以太坊。
—
About the author
The ultimate guide to understand why Ethereum is not just another cryptocurrency.
了解为什么以太坊不只是另一种加密货币的终极指南

Although ‘Bitcoin’ and ‘Ethereum’ are terms that are often paired together, the reality is that they are vastly different. The only thing Ethereum shares with Bitcoin is that it’s a cryptoasset running on top of blockchain.
Instead of being just a cryptocurrency, like Bitcoin, Ethereum also has features which effectively makes it a huge decentralized computer.
虽然’比特币’和’以太坊’是经常被搭配在一起的术语,但现实是它们有很大的不同。以太坊与比特币的唯一共同点是,它是一种运行在区块链之上的加密资产。
与比特币一样,以太坊不仅仅是一种加密货币,它还具有一些功能,这些功能实际上使它成为一个巨大的去中心化的计算机。
要了解以太坊,必须了解区块链的工作原理。如果你已经了解了,或者已经读过我的了解区块链的终极指南,请放心直接进入下一节。
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain, simply put, is a database. It’s an ever growing database of certain kind of data and has quite remarkable properties:
1.Once data is stored in the database, it can never be modified or deleted. Every record on a blockchain is permanent for eternity.
2.No single individual or organization maintains the database; several thousand individuals do, and everyone has a copy of the database with themselves.
什么是区块链?
区块链,简单地说,就是一个数据库。它是一个不断增长的某种数据的数据库,具有相当显著的特性。
1. 一旦数据被存储在数据库中,它就永远不能被修改或删除。区块链上的每条记录都是永久的,是永恒的。
2.没有一个人或组织维护数据库;几千个人在维护,每个人都有一份数据库的副本。
To understand how several people are able to keep their copies of the database in sync with everyone else, imagine there are ten individuals in a network. Everyone is sitting with an empty file folder and an empty page in front of them. Whenever anyone does something important in the network, like transferring money, they announce it to everyone in the network.
为了理解几个人如何能够使他们的数据库副本与其他人保持同步,想象一下在一个网络中有十个人。每个人面前都坐着一个空文件夹和一个空页面。每当有人在网络中做一些重要的事情,比如转账,他们就会向网络中的每个人宣布。

Everyone makes a note of the announcement on their pages until the page is filled. When it does, everyone has to seal the contents of the page by solving a mathematical puzzle. Solving the mathematical puzzle ensures that everyone’s page had same contents and that they can never be modified. Whoever does it first, gets rewarded with some amount of cryptocurrency.
每个人都在自己的页面上记下公告的内容,直到页面被填满。当它被填满时,每个人都必须通过解决一个数学谜题来密封页面的内容。解决这个数学谜题可以确保每个人的页面都有相同的内容,并且永远不会被修改。谁先做到这一点,谁就能得到一定数量的加密货币的奖励。
Once the page is sealed, the page is added to the file folder, a new page is brought out and the process continues forever.
一旦这一页被封存,这一页就会被添加到文件夹中,新的一页就会被拿出来,这个过程会永远继续下去。

Blockchain
As time passes, these pages (blocks) that contain important records (transactions) are added to the folder (chain), thus forming the database (blockchain).
随着时间的推移,这些包含重要记录(交易)的页面(区块)被添加到文件夹(链)中,从而形成数据库(区块链)。
What does a blockchain store?
A blockchain can be used to store any kind of data, and the kind of data a blockchain stores, gives it its value. Bitcoin’s blockchain stores the records of financial transactions, therefore, making it analogous to a currency like dollars or pounds. Bitcoins serve no additional purpose than what dollars serve. Ethereum is different.
Ethereum is not merely a currency like dollars, pounds or bitcoin. Ethereum has a purpose higher than just being a currency. Ethereum is this:
区块链存储什么?
区块链可以用来存储任何种类的数据,而区块链所存储的数据种类,使其具有价值。比特币的区块链存储的是金融交易的记录,因此,使其类似于美元或英镑这样的货币。比特币没有比美元更多的用途。以太坊则不同。
以太坊不仅仅是一种像美元、英镑或比特币一样的货币。以太坊有一个比仅仅作为货币更高的目的。以太坊就是这样。

Ethereum is basically a huge computer! However it’s an extremely slow one — about five to 100 times slower than regular computers today — and very expensive. The ‘Ethereum computer’ has about the same power as one of the rare90’s smartphones; so it can’t really do much more than some very trivial things.
以太坊基本上是一个巨大的计算机!但它是一个非常慢的计算机–比今天的普通计算机慢5-100倍,而且非常昂贵。以太坊电脑 “的功率与90年代罕见的智能手机之一差不多;因此,除了一些非常琐碎的事情,它真的不能做得更多。
That doesn’t really sound so impressive, so why is there so much hype around Ethereum? Well, that’s a really good question. Ethereum is taking the world by storm because it’s a completely decentralized computer that is distributed across the globe. Understanding how Ethereum’s blockchain works will reveal how it acts like a world computer.
这听起来并不那么令人印象深刻,那么为什么以太坊周围有这么多的炒作呢?嗯,这真是个好问题。以太坊正在风靡世界,因为它是一个完全去中心化的计算机,分布在全球各地。了解以太坊的区块链是如何工作的,将揭示它是如何像世界计算机一样行事的。
How does Ethereum work?
Like any other blockchain, Ethereum needs several thousand people running a software on their computers to power the network. Every node (computer) in the network runs something called Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Think of EVM as a operating system that understands and executes the software written in Ethereum specific programming language. The software/apps executed by Ethereum Virtual Machine are called ‘smart contracts.’
以太坊是如何工作的?
像其他区块链一样,以太坊需要几千人在他们的电脑上运行一个软件来驱动网络。网络中的每个节点(计算机)都运行着一种叫做以太坊虚拟机(EVM)的东西。把EVM想象成一个操作系统,理解并执行以太坊特定编程语言编写的软件。由以太坊虚拟机执行的软件/应用程序被称为 “智能合约”。
To get anything done on this world computer, you need to pay a price. However, you don’t pay it in regular currency like dollars or pounds. Instead, everything has to be paid with a cryptocurrency native to the network, called ether. Ether is exactly like bitcoin except that it can also be used to pay for executing smart contracts on Ethereum.
要在这个世界的电脑上完成任何事情,你需要付出代价。然而,你不是用美元或英镑等常规货币支付。相反,一切都必须用网络中原生的加密货币支付,称为以太币。以太币与比特币完全一样,只是它也可以用来支付执行以太坊的智能合约。
A human being and a smart contract are both seen as users on Ethereum. Whatever a human user can do, a smart contract can do too, and then some.
人类和智能合约都被视为以太坊的用户。人类用户能做的事,智能合约也能做,甚至更多。

Smart contracts act exactly like any other human user in the network. Both of them can send and receive ether just like any other currency.
智能合约的行为与网络中的其他人类用户完全一样。他们都可以像其他货币一样发送和接收以太币。

But unlike human users, smart contracts can also execute a predefined computer program to perform various actions when triggered. To understand the power of a smart contract, let’s consider an example.
但与人类用户不同的是,智能合约也可以执行预定义的计算机程序,在被触发时执行各种行动。为了理解智能合约的力量,让我们考虑一个例子。
Power of smart contracts
Imagine you and I place a bet about tomorrow’s weather. I bet that it’ll be sunny tomorrow while you bet it’ll be rainy. We agree that the loser has to give the winner $100. How can we do this and ensure that the loser will keep his promise? I can think of three distinct ways:
智能合约的力量
想象一下,你和我就明天的天气打了个赌。我打赌明天会是晴天,而你打赌会是雨天。我们约定,输家必须给赢家100美元。我们怎样才能做到这一点,并确保输家会遵守承诺呢?我可以想到三种不同的方法。
1. Trust each other
The simplest way to do this would be to trust each other. If we’ve been friends for a long time now, trusting each other is pretty easy. I know where you live and you know all kinds of embarrassing stuff about me. But things get more difficult if we’re complete strangers. You have no reason to trust me and I have no reason to trust you.
1. 互相信任
最简单的方法是相互信任。如果我们现在已经做了很长时间的朋友,信任对方是很容易的。我知道你住在哪里,你也知道关于我的各种令人尴尬的事情。但如果我们是完全陌生的人,事情就会变得更加困难。你没有理由相信我,我也没有理由相信你。
2. Sign a legal agreement
Another plausible way is to formulate our bet as a legal agreement. We’ll both sign an agreement that defines all the terms of our bet in detail — including what happens if the loser violates the agreement.
The agreement would makes us legally obligated to pay the winner, but it wouldn’t serve any practical purpose because forcing the agreement through the legal route would be more expensive than what the bet was worth.
2. 签署一份法律协议
另一个合理的方法是将我们的赌注拟定为一份法律协议。我们双方将签署一份协议,详细定义我们赌注的所有条款–包括如果输家违反协议会发生什么。
该协议将使我们在法律上有义务支付赢家,但它不会起到任何实际作用,因为通过法律途径强制执行该协议的费用会比赌注的价值更高。
3. Get help from a mutual friend
We could find a mutual friend who we both trust and we’d both give him/her $100 each for safekeeping. The nextday, he/she would check the weather and give the total $200 to whoever won the bet. Simple and easy, except that it isn’t: What if the trusted friend runs away with $200?
Now we have three different ways of doing the bet but each option has its shortcomings. Because we are strangers, we cannot trust each other. Forcing a legal agreement will be so expensive that it wouldn’t be practically feasible. Getting help from a mutual friend brings up the question of trust again.
Ethereum’s smart contract can save the day in such a situation. A smart contract is like the trusted mutual friend but written in code. Ethereum allows us to write a software that accepts ether worth $100 from both of us, and then the next day, uses the open weather API to check the weather and transfer the total ether worth of $200 to the winner.
3. 从一个共同的朋友那里获得帮助
我们可以找到一个共同的朋友,我们都信任他/她,然后我们都给他/她每人100美元作为保管费。第二天,他/她会检查天气,并将总额200美元交给赢得赌局的人。简单而容易,除了它不是。如果那个值得信赖的朋友拿着200美元跑了怎么办?
现在我们有三种不同的打赌方式,但每个选项都有其缺点。因为我们是陌生人,我们不能信任对方。强行签订法律协议的费用会很高,实际上是不可行的。从共同的朋友那里获得帮助又带来了信任的问题。
在这种情况下,以太坊的智能合约可以拯救世界。智能合约就像受信任的共同朋友,但用代码编写。以太坊允许我们写一个软件,接受我们两个人的价值100美元的以太坊,然后在第二天,使用开放的天气API检查天气,并将总价值200美元的以太坊转移给赢家。

Once a smart contract has been written it cannot be edited or altered in any way. Therefore, you can be sure that whatever the contract dictates, it will be executed no matter what.
But how is a smart contract executed? And how does it relate to blockchain?
一旦智能合约被写入,它就不能以任何方式被编辑或改变。因此,你可以确信,无论合同规定什么,它都会被执行。
但智能合约是如何执行的?它与区块链又有什么关系?
How does smart contract relate to blockchain?
Whenever a smart contract is executed, it records the information about the execution on a block as a transaction. On a very high level, a transaction on Ethereum blockchain looks like this:
智能合约与区块链的关系如何?
每当智能合约被执行时,它就会把执行的信息记录在一个区块上,作为一个交易。在一个非常高的水平上,以太坊区块链上的交易看起来像这样。

The fields are self explanatory except the last one. The ‘data’ field is what gives Ethereum its unique power. The ‘data’ field is used to record creation and execution of smart contracts as a transaction. Any given block on the Ethereum blockchain can contain three kind of transactions:
除了最后一个字段,其他字段都是不言自明的。数据 “字段是赋予Ethereum独特力量的原因。数据 “字段被用来记录智能合约的创建和执行,作为一项交易。以太坊区块链上的任何特定区块可以包含三种交易。
1. Regular transfers of ether from one user to a human user
These are the regular bitcoin-like transactions in the network. If you send ether directly to your friend the data field will be left empty.
1. 一个用户向一个人类用户定期转移以太币
这些是网络中类似比特币的常规交易。如果你直接向你的朋友发送以太币,数据字段将被留空。

2. Transfers of ether from one user to no one
When a transaction without a recipient is made, it means that the purpose of the transaction is to create a smart contract in the network using the contents present in the ‘data’ field. The ‘data’ field contains the software code that will be made to act like any other user in the network.
2. 从一个用户转移到没有人的地方的以太币
当一个没有收件人的交易发生时,这意味着该交易的目的是在网络中使用’数据’字段中存在的内容创建一个智能合约。数据 “字段包含的软件代码将被制成与网络中任何其他用户一样的行为。

3. Transfers of ether from a user to a smart contract
Whenever a user (or a smart contract) wants to execute a smart contract, he/she/it is required to make a transaction to the smart contract and put the instructions for the execution in the ‘data’ field.
3. 从一个用户到一个智能合约的以太币转移
每当一个用户(或一个智能合约)想要执行一个智能合约,他/她/它需要向智能合约进行交易,并将执行指令放在 “数据 “字段中。

Just like in any other blockchain, whenever any of the three events mentioned above happen, it’s announced to the whole network and everyone makes a note of it. In addition to making note of it, each node also executes the instructed smart contract to bring the state of their EVM in sync with the rest of the network.
Each node executes a piece of software, thus, making the whole network act as a giant (but slow) distributed computer. Every tiny execution is then stored on the blockchain to make it permanent.
就像其他区块链一样,每当上述三个事件中的任何一个发生,都会向整个网络宣布,每个人都会记下它。除了记下它之外,每个节点还执行指示的智能合约,使其EVM的状态与网络的其他部分同步。
每个节点执行一个软件,因此,使整个网络作为一个巨大的(但缓慢的)分布式计算机。然后,每一个微小的执行都被储存在区块链上,使其成为永久性的。
Wait, I’ve heard about something called Gas — what’s that?
I told you that the user using a smart contract must pay a certain price to execute it. This price is paid to the node that actually spends memory, storage, computation and electricity to execute the smart contract.
等等,我听说过一个叫Gas的东西–那是什么?
我告诉你,使用智能合约的用户必须支付一定的价格来执行它。这个价格是支付给实际花费内存、存储、计算和电力来执行智能合约的节点的。
To calculate the prices of smart contracts, every statement has an assigned cost to it. For example, if you execute a statement that uses the node’s memory, those type of statements have a specific cost. If you execute a statement that uses the node’s disk storage, those kind of statements have a specific cost attached to them. The unit in which the cost is defined is called Gas. Eventually, Gas is converted to ether using an exchange rate.
为了计算智能合约的价格,每个语句都有一个分配的成本。例如,如果你执行一个使用节点内存的语句,那些类型的语句有一个特定的成本。如果你执行一个使用节点的磁盘存储的语句,那些类型的语句有一个特定的成本附加在它们身上。定义成本的单位被称为Gas。最终,Gas通过一个汇率被转换为以太币。
Whenever you execute a smart contract, you have to define the maximum Gas to be consumed. The execution will stop either when the execution is completed or when the Gas Limit is reached. This is done to avoid infinite loops in smart contracts, preventing the program getting stuck executing a set of statements repeatedly without proceeding further.
每当你执行一个智能合约时,你必须定义所要消耗的最大气体。当执行完成或达到Gas Limit时,执行将停止。这样做是为了避免智能合约中的无限循环,防止程序被卡住重复执行一组语句而无法继续下去。
Such situations occur because of programmer’s carelessness. With every repetition, some of the assigned Gas will be used, thus making any infinite loop a finite one. It doesn’t make any sense for a node to be stuck in execution because of a programmer’s mistake. The concept of Gas solves this problem.
这种情况的发生是因为程序员的粗心。随着每一次重复,一些分配的Gas将被使用,从而使任何无限循环成为有限循环。一个节点因为程序员的错误而被卡在执行中是没有任何意义的。气体的概念解决了这个问题。
And that, ladies and gentleman, is Ethereum
Ethereum isn’t just a cryptocurrency to be traded; its real value lies in its purpose. Ethereum’s purpose is to allow the owner to use the distributed world computer that several thousand nodes are powering.
Of course, because every tiny statement has to be executed by every node in the network, the decentralized, distributed computer becomes slow and expensive. But slow compared to what? The faster but centrally controlled servers.
To enjoy the lower costs of using a centralized computer, we give them the power to control us. If the central computer (server) goes down or gets hacked, it takes down with it all the clients attached to it. A decentralized computer will only go down if every single node goes down, making it a computer that will always be available. Wherever there’s internet, there’s Ethereum.
而这,女士们,先生们,就是以太坊
以太坊不仅仅是一种可以交易的加密货币;它的真正价值在于其目的。以太坊的目的是允许所有者使用几千个节点所提供的分布式世界计算机。
当然,由于每一个微小的语句都必须由网络中的每一个节点来执行,去中心化的分布式计算机变得缓慢而昂贵。但是,与什么相比慢呢?更快但集中控制的服务器。
为了享受使用集中式计算机的低成本,我们给了他们控制我们的权力。如果中央计算机(服务器)瘫痪或被黑客攻击,它就会连带着所有连接在它上面的客户端一起瘫痪。一个分散的计算机只有在每个节点都瘫痪的情况下才会瘫痪,这使得它成为一个永远可用的计算机。只要有互联网的地方,就有以太坊。
—
About the author
Mohit Mamoria is the CEO ofgodtoken.org and editor of a weekly newsletter, Unmade, which delivers one startup idea from the future to your inboxes.
 一洼田
一洼田